
Intensity-based point cloud from the scanner. View of one single scan.


Within this project of Cooperation between the Universidad Politécnica de Valencia and the Hachemita University, the following objectives were established:
Results show that:

Intensity-based point cloud from the scanner. View of one single scan.

Point clouds coloured from the scanner. General view after registration.

Overall photorealistic model of the Djin Block No. 9: Western and Southern sides (left); Northern and Western sides (right).
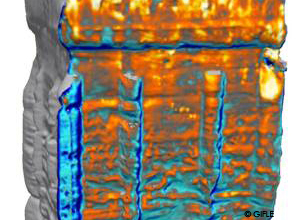
Detail of the thermorealistic model of the Djin Block No. 9. Eastern side.

Visible orthoimage. Eastern side orthographic view of the Djin Block No. 9.
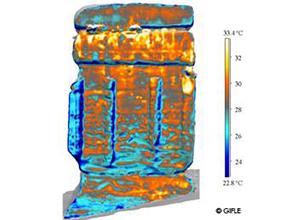
Thermal orthoimage. Eastern side orthographic view of the Djin Block No. 9 at 08:15.
Navarro, S., Seguí, A.E., Portalés, C., Lerma, J.L., Akasheh, T. and Haddad, N., 2009. Integration of TLS data and non-metric imagery to improve photo models and recording. A case study on Djin Block No. 9, Petra (Jordan). In: R. Sablatnig, M. Kampel and M. Lettner (Editors), 15th International Conference on Virtual Systems and Multimedia (VSMM). IEEE Computer Society, 9-12 September, Vienna, Austria, pp. 58-63.
Cabrelles, M., Galcerá, S., Lerma, J.L., Akasheh, T. and Haddad, N., 2009. Integration of 3D laser scanning, photogrammetry and thermography to record architectural monuments, 22nd CIPA Symposium, Kyoto, 11-15 October, Japan.
Cabrelles, M. , Seguí, A. E., Navarro, S., Galcerá, S., Portalés, C. and Lerma, J. L., 2010. 3D Photorealistic modelling of stone monuments by dense image matching. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Vol. XXXVIII, Part 5. Commission V Symposium, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, pp.121-124.
Akasheh, T. S., Lerma, J. L., Cabrelles, M. and Haddad, N., 2010. The multispectral and 3D study of the Obelisk Tomb in Petra, Jordan. 3rd International Conference dedicated on Digital Heritage (Ioannides, M., Fellner, D., Georgopoulos, A., Hadjimitsis, D., Eds.). Short Papers, pp. 35-40, 8-13 November, Limassol, Cyprus.
Lerma, J. L., Akasheh, T., Haddad, N., Cabrelles, M., Seguí, A. E. and Navarro, S., 2010. Stone surface temperatura analysis on the Djin Block No. 9 in Petra (Jordan). Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Science and Technology in Archaeology and Conservation, pp. 224-232, Amman-Petra, 7-11 December, Jordan.